Nov 27, 2018 18:30 UTC
| Updated:
Nov 29, 2018 at 04:51 UTC
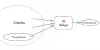
Classification of Blockchains
It was Bitcoin that introduced Blockchain Technology to the world. The technology is gradually making its mark in every sector, be it Blockchain in Agriculture, Real Estate, Healthcare, Education and that’s just the tip of the iceberg.
This all started with the Bitcoin Whitepaper released by Satoshi Nakamoto (a pseudonym of either a person or a group of people) in 2008. The first bitcoin block was mined in 2009. Since Bitcoin protocol is an open source, everyone is free to take the protocol, fork it and start their own version of Peer-to-Peer money.
A number of so-called altcoins emerged out and even tried to be better and faster than Bitcoin. Soon the code was not just altered to create better cryptocurrencies, but there are a few projects which tried to alter the idea of blockchain beyond the blockchain use case in payments.
Types of Blockchain
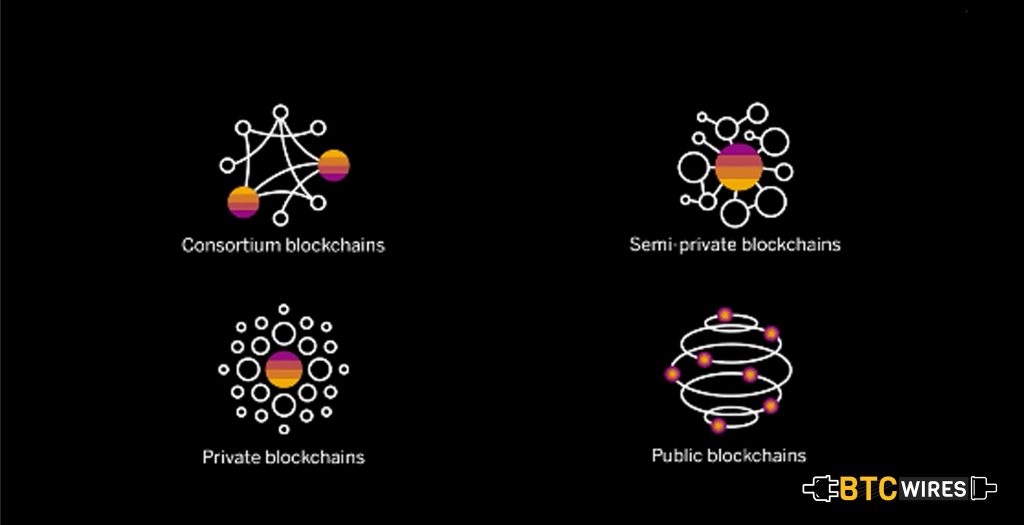
Well, this idea emerged that the Bitcoin Blockchain could be used for all types of value transactions or agreements like Peer-to-Peer energy trading, Peer-to-Peer insurance, Peer-to-Peer ridesharing and more. Mastercoin and Colored Coins attempted to solve that problem depending on the different consensus Blockchain Protocol. The Ethereum project decided to its own blockchain that has very different properties than that of Bitcoin. It was done by decoupling the smart contract layer from the core blockchain protocol that offers a radical new approach for creating online markets as well as programmable transaction known as Smart Contracts.
Even several private institutions, such as banks, realized that they could also use the core idea of blockchain as a DLT (Distributed Ledger Technology), and create a permissioned blockchain where validator is a member of separate legal entities of the same organization. However, the term blockchain in the context of the permissioned private ledger has been very controversial and disputed. It is for this reason, why the term distributed ledger technologies emerged as a more general term.
Private Blockchain is valuable to solve efficiency, fraud and security issues within traditional financial institutions, however just steadily. It’s not likely that this blockchain type will revolutionize the financial framework. However, Public Blockchain holds the potential to supplant most elements of conventional financial institutions with programming, on an elementary reshaping the manner in which the financial system works out.
Let’s have a closer look at each type…
Public Blockchain

It is a type of blockchain that allows everyone from anywhere to join the network and reserve equal rights to add nodes for everyone. One can join this network whenever they feel like, and they will have complete authority like the others in the network.
This model was suggested back in 2009 by Satoshi Nakamoto. It is often referred to as the mother technology that corporations started following, twitched the nature of decentralized ledger and brought Private Blockchain into the light.
Examples of Public Blockchain –
Private Blockchain
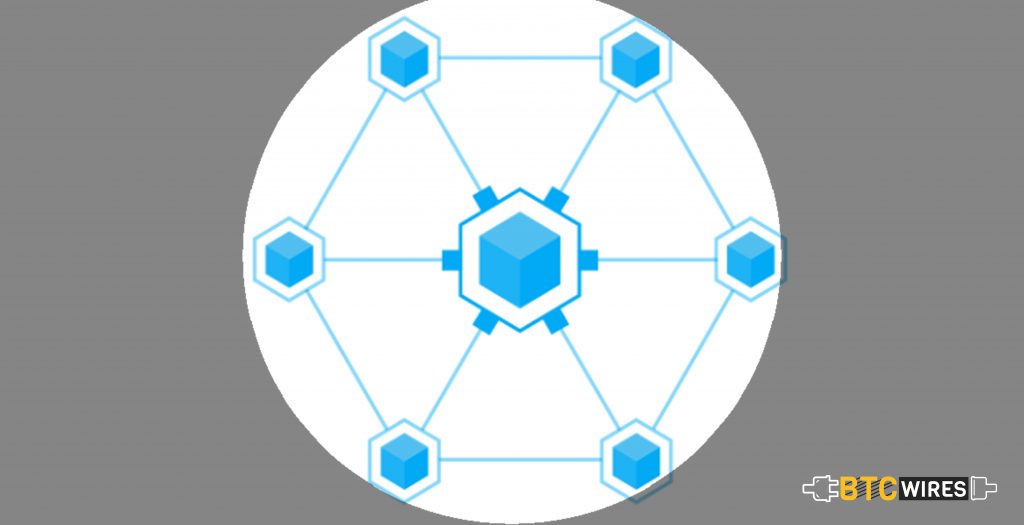

This type of blockchain is based on private properties of individuals or organizations. Unlike Public Blockchain, this blockchain has the in-charge who takes care of all the necessities, for example, whoever is being given access to reading, writing, etc.
In Private Blockchain, the consensus is achieved on through the central in-charge who is responsible for giving mining rights to the individuals. It is his choice whether he wants to give the rights to anyone or not give at all by his choice. This particular nature of Private Blockchain makes it centralized whereby many rights are exercised in a central trusted party.
There have been many debates on whether or not this type of blockchain to be called a Blockchain, as it beats the whole purpose of blockchain that was introduced by Bitcoin in 2008.
Examples of Private Blockchain –
- Multichain and MONAX
Consortium Blockchain
This is unique in itself. Consortium Blockchain varies from its counterparts. Though it is permissioned, yet not everyone could start using this. This type of blockchain has been articulated as being the semi-decentralized type of blockchain, meaning it doesn’t grant the control to any single entity, but rather a group of only authorized individuals.
The different consensus protocols used in blockchain are, with Consortium Blockchain, likely to vary from public blockchain. Different from the other two types, the participants of this type of blockchain are most likely to be a group of authorized nodes on the network. Working this way, Consortium Blockchain has the security features necessary in public blockchain while still offering much control over the network.
Examples of Consortium Blockchain –
- Corda, B3i (Insurance), EWF (Energy), R3 (Banks), etc.
Conclusion!
Did you get the understanding of all three types of Blockchain? If you compare Public Blockchain with the other two types, you will always be confused. All three are different from one another. Their names are different; their purpose is different, and they work differently.
Because of their unique nature, different types of blockchain will be used for different types of industry whenever required.
It’s simple! If you need privacy and control, then Private and Consortium Blockchain will be a good going. In case you need openness, then Public Blockchain is the must. This is the reason why different people are discussing different uses of blockchain technology across numerous industry verticals.
Here are a Few Articles for you to Read Next: